In Malaysia, climate changes pose a challenge to the country’s water resource management and security, coastal resources,
agriculture and food supply, urban and infrastructure resilience, public health, as well as forestry and biodiversity.
In Malaysia, climate changes pose a challenge to the country’s water resource management and security, coastal resources,
agriculture and food supply, urban and infrastructure resilience, public health, as well as forestry and biodiversity.
Malaysia does not provide a breakdown of their sectoral targets but they do mention sectors, gases, categories and pools covered by the nationally determined contribution, including, as applicable, consistent with IPCC guidelines which are:
Sectors: Energy, Industrial Processes and Product Use, Waste, Agriculture, LULUCF
GHGs: Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide (N2O), Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), Perfluorocarbon (PFCs), Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3)
Malaysia has their own National Steering Committee on Climate Change, in charge for developing their NDC targets. The country has also established the Majlis Tindakan Perubahan Iklim Negara (MTPIN) in 2023 tasked to coordinate and oversee national climate initiatives. Other than the National Adaptation Plan, the country is also formulating the Long-Term Low GHG Emission Development Strategies as the baseline for their work. Through cross sectoral efforts, Malaysia is exploring and optimise the financing mechanism and technological assessment and capacity development for climate change impacted sectors.
In August 2023, the Malaysian government published the National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) as the basis of their energy transition plan. Other than that, the country have also published the Malaysia Renewable Energy Roadmap (MyRER).
| Topic | Title | Year | Issuing Ministry |
| National Climate Change Policy 2.0 | 2024 | Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Sustainability | |
| Circular Economy Policy Framework for the Manufacturing Sector in Malaysia | 2024 | Ministry of Investment, Trade, and Industry | |
| New Industrial Master Plan 2030 | 2023 | Ministry of Investment, Trade, and Industry | |
| National Energy Policy (2022- 2040) | 2022 | Ministry of Economy | |
| National Automotive Policy 2020 | 2020 | Ministry of Investment, Trade, and Industry | |
| National Energy Efficiency Action Plan 2015 | 2015 | Ministry of Energy, Green Technology, and Water | |
| National Renewable Policy & Action Plan 2010 | 2010 | Ministry of Energy, Green Technology, and Water | |
| National Policy on Climate Change 2009 | 2009 | Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment | |
| National Green Technology Policy 2009 | 2009 | Ministry of Energy, Green Technology, and Water | |
| National Biofuel Policy 2006 | 2006 | Ministry of Plantation Industries and Commodities |
Gas and oil become the dominant of TPES, and coal has increased by 2.46% from 885,276 TJ in 2020 to 907,663 TJ in 2021 [1].
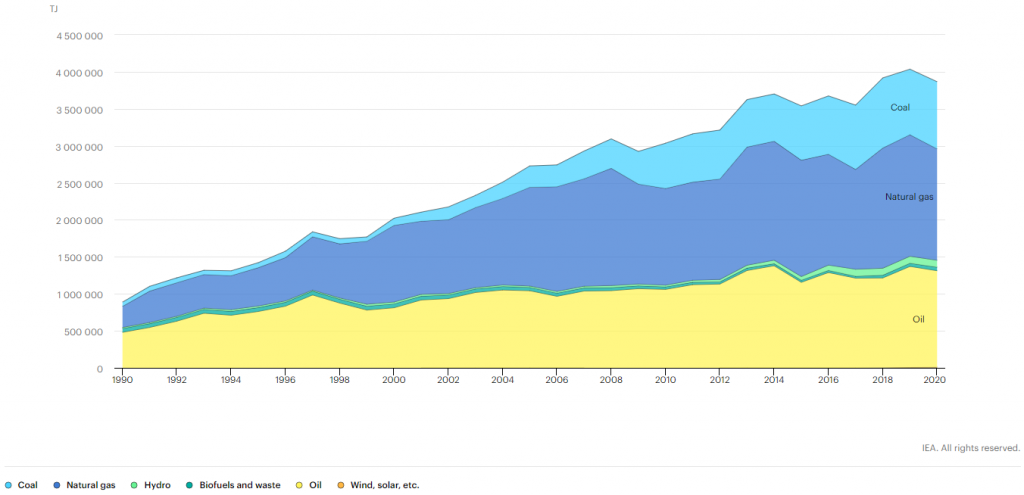 [1] IEA: The total energy supply by source
[1] IEA: The total energy supply by source
Oil products are the largest consumers in TFEC, and it has been increasing gradually since 2000, mainly due to high demand from the transport sector. Whereas electricity is the second largest consumer of the end users. Malaysia’s Coal Consumption was reported at 21.122 million TOE in Dec 2018 [2].
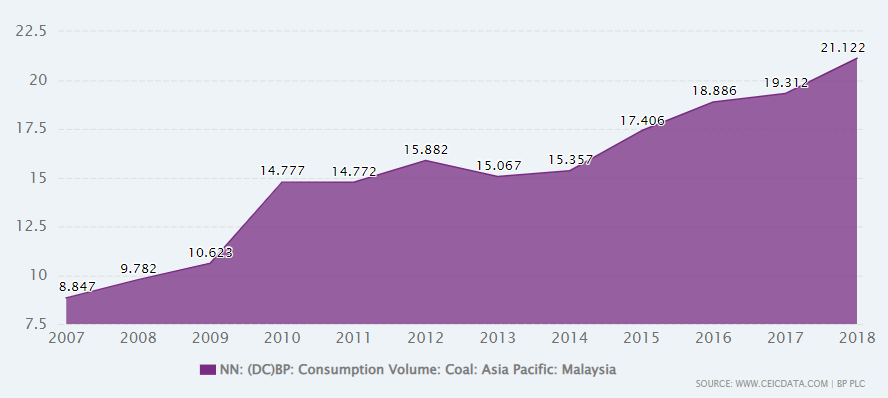
[2] CEIC: Malaysia Coal Consumption
